Token ring networks
In the ring topology, all the PC`s are connected up in a ring, with each network card having two ports - an input port, and an output port.
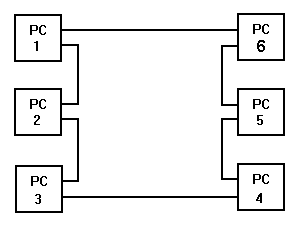
The data flow is always in the same direction around the ring.
The logical control mechanism is three bytes of a particular series of bits, which form a token - when a PC receives this token, it is free to transmit data onto the ring.
The PC then splits the token, takes the first byte, modifies the second byte, inserts the data it wants to transmit, adds the last byte of the token, followed by a end-of-frame one byte flag and sends the whole lot off.
The data sent includes the actual information data, as well as the address of the intended recipient, and the address of the sender. It can also contain all the packaging information from a higher layer, such as TCP/IP, NetBIOS, or IPX.
This packet of data then travels round the ring until it gets to the intended recipient.
The recipient amends the data packet by changing some particular bits, and then sends the data packet on round the ring, until it reaches the original sender.
The sender reads the control bits to check that it is the same data as was originally sent, and if correct, the sender PC removes the data, and sends a new token off round the network, for other nodes to use.
Each PC acts as a node in the ring, it takes in the incoming data, reads it to see if it is the intended recipient, and if not, reprocesses the data and sends it on to the next PC, or node.
There are two standards for data transfer speed on token ring - 4 Mbps and 16 Mbps.
Future developments in token ring will allow a speed of 100 Mbps, and be known as high speed token ring. Equipment will become triple standard, working at all three speeds.
Token ring versus Ethernet
Token ring has a number of advantages over Ethernet based networks.
These include :-
a larger packet size of 4550 bytes
there is a guaranteed maximum delay time that any node will have to wait, before it can transmit
the network can be used to almost 100% of its theoretical capacity without exceeding known longest access times
all nodes can have an equal share of access time to the network
bits can be set in the token to indicate priority levels - a PC can only use the token if it has a higher priority than the code in the token. As there are three priority bits, there can be eight priority levels.
In contrast, Ethernet based networks :-
have a much smaller packet size of 1518 bytes
cannot predict how long any node will have to wait, before it can transmit successfully
grind to a halt as traffic increases
can suffer from one node hogging the network, by transmitting a large number of packets in succession
cannot have priority levels
Token ring networks also have disadvantages compared to Ethernet based networks :-
there is not actually a ring of cable in a token ring network, it is actually a series of individual links between PC`s, which form a closed loop - if any one of these individual links is broken, the network ceases to function
if any one of the network adapters ( the name given to the network interface cards within each PC in a token ring ) ceases to operate, then, again, the network ceases to operate
modifications cannot be made to the network without breaking the loop, and thus stopping the network from operating
Network management
Within a token ring network, when the network is first configured, one of the PC`s on the network is designated the status of active monitor, and the others as standby monitors.
The active monitor oversees the operation of the network, checks the token is okay, and controls timing.
If the active monitor fails for any reason, one of the standby monitors take over.
The packet contains a beacon flag, so that if there is a network malfunction, such as a network adapter not receiving any data, or mis-timed data, a network adapter can set this flag, and diagnostic software can be used to locate the source of the problem.
Some of the packets of data circulating around the network loop are not originated by the PC`s. They are originated by the network adapters, and are used for network management purposes, not for data transfer.
Physical layout
Although it is always a logical ring, token ring networks are often wired using hubs, or MSAU`s - multi-station access units and wired using unscreened twisted pair.
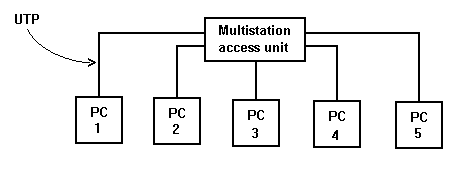
Although this looks like a hub as is used on ethernet, it is different, as the inside of the multi-station access unit looks like
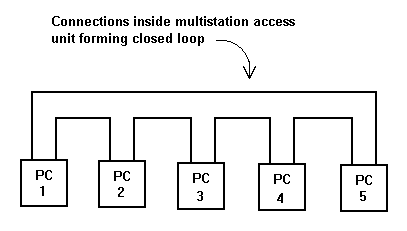
This means that, like ethernet wired in 10-base T, the cabling can be hidden behind walls, coming out in sockets.
However, unlike ethernet, disconnecting a PC without looping will disable the whole network.
Finally, like ethernet, token ring networks can use bridges, but they have to be designed specifically for token ring networks.
© 1998 Ron Turner
Return to the network home page